Division – How to Teach, Post
- On Feb, 27, 2018
- Mary Keating
- Blog
Division – How to Teach
New method versus old methods: Anyone can teach division to Middle Primary School children. Methods have changed a bit over the years but they are not necessarily better. We can’t tell if they are better until we see results over time.
The new strategy used in classrooms involves:
- working from the top down rather than bottom up in addition and subtraction.
- It also involves crossing out a number and writing another number, in every column except the units.
Children continue into the higher levels of primary school using this method of crossing out numbers and changing them. As a result many kids don’t move into quicker and better methods. Nor do they learn to trust their memory. Students should be taught to let go of this practice as they move through Grades 5 and 6.
The top down method changes the language children use as well. They will say 9 (on the top) take away 5 (on the bottom). Students can say 5 (on the bottom) from 9 (on the top).
Using the bottom to top method for adding, subtracting and multiplying makes learning easier.
When teaching multiplication students must work from the number at the bottom.
6 3 2
x 5
Many children are saying 2 x 5 because they are accustomed to working from the top. But here they must multiply by 5. Yes, the answer is the same but clarity of thought is missing as maths becomes more complex.
Teaching division may be better left until around Grade 4. The advantages are:
-
-
- the child learns faster because of age, and it
- side-steps the time-wasting and confusing crossing out of numbers that students have become used to.
-
So, how to teach division
>>Explain to the child that division is the only one of the four functions (+, -, x, /) where you work from the Thousands or Hundreds Column and not the Ones Column (units). This is why it is the last function that we teach.
You want to divide 5 into 5635. 5 / 5635.
Divide 5 into 5 = 1.
Divide 5 into 6 = 1 and 1 remainder. Put a small 1 above and in front of the 3. So the child then can read the number 13.
Divide 5 into 13 = 2 and 3 remainder.
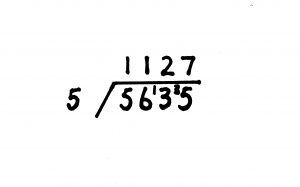
Put a small 3 above and in front of the 5. So the child then can read the number 35.
Divide 5 into 35 = 7.
The answer is 1127.
If there is a zero in the number, it must be put into the answer. Kids sometimes forget this point.
An example is at left 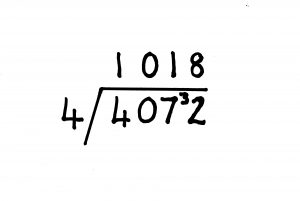
The Worksheets for Grade 4 have lots of practice in doing this kind of sum in the 3x, 4x and 5x tables. Grade 4 children learn the 6x, 7x and 8x times tables progressively. But the division practice in these worksheets uses the tables they have already mastered.
Link To Merlin Maths : There are several maths packages on this site for Grade 4. Some are free packs.
Merlin Maths is one and here is the link. “Merlin Maths for Grade 4”
Maths Action series by W. Camage and M. McDonald is one of many excellent maths textbooks. These are reasonably priced and can be purchased online. There is one for each year level.
Links: Maths Words Grades 4-6, List “Multiples” Maths Practice Grade 5-6 “Merlin Maths for Grade 4”, “Maths Hatch for Grade 4”, “Factors and Fractions” Maths Grade 4